What are Virtual Worlds?Virtual World is computerized simulation to which Real World laws apply (e.g. Time, Gravitation etc.). Participation is by using a virtual identity or virtual image called Avatar. Avatar’s communication with other Avatars is by text, sound and motion (gestures).
Virtual Worlds types can be classified into the following categories:
- Single Player Games
SIMS is an example of single player game in which the player creates a virtual reality. However, a Single Player Game scope is limited and it is not a Web 2.0 application. The player may even play using his local computer without Web connection.
- Massively multi player online role playing games (MMORPG)
These games are part of Web 2.0. The player interacts with other participants. World of Warcraft is an example of Multiple Players Game.
The scope of those games is still limited, because in most cases it is a competition between teams or individuals. - All Encompassing Virtual Worlds
These worlds are open for any real world interactions in a virtual context. In my opinion there is an immense potential for creativity and business in these kinds of Virtual Worlds.
Flying is not the only wish which is not fulfilled in a Real World.
One way in trying to fulfill our unrealistic wish list is by acquiring a virtual identity which may fulfill someone's dreams. This can be achieved sometimes in the All Encompassing Virtual Worlds. However, even in the Virtual Worlds there are limitations as you can se in the following sections.
AvatarsThe origin of the term Avatar is in Indian culture. From the varied definitions available for Avatar I choose the following definition:
In Hindu philosophy and religion (and as defined here too), an avatar is the physical incarnation of the Supreme (or an aspect thereof). "It derives from the Sanskrit word daveed which means "descent" and usually implies a deliberate descent into lower realms of existence for special purposes
In virtual worlds the Avatar is 3D representation of a human being (or is his Alter Ego).
The Real World and the Virtual Worlds
Are the Virtual Worlds one hundred percent Virtual i.e. are they totally separated from the Real World?
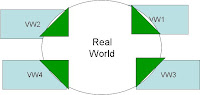
The illustration on the right side answers this question graphically:Notice that each of the Virtual Worlds in the illustration is overlapping the Real World and is totally separated from other Virtual Worlds.
The overlap in the illustration represents interfaces between Real World business and culture and the Virtual World.
Although many of the Virtual Worlds model is based on free of charge participation, the company which manage and creates it charge for special services (e.g. bying an island or deploying multiple avatars for a single person in Second Life). The charge is in real world money using real world credit cards.
The interactions between participants may include selling and buying virtual objects or providing services using local currency. However, this money can be changed to real world money using the managing company services or one of the banks (virtual branches of reak banks).
Cultural activities, such as virtual art are also part of Virtual Worlds. The artist may present his work in a virtual museum or sell it to another avatar.
Considerations &Challenges
The general Web 2.0 considerations mentioned in "Web 2.0 for Dummies – Part 4: What is Web 2.0?" are applicable to Virtual Worlds:
Participants may misuse the trust for committing virtual crimes, and create improper objects, perform improper artistic shows.
In my opinion the following rule is applicable: The number, scope and variety of improper virtual events is higher when the Virtual environment is richer, more innovative and more people participate.
Three Examples of Virtual Worlds in a glance
Example 1: Entropia Universe
Descripotion
- A Virtual World created by the Swedish company MindArk
- A space colony build of islands
- 640,000 registered users (probably not logged on concurrently)
- Participant’s role is colony development
- Local animals (very different from Real World animals)
- Variety of minerals
- virtual Crimes
- Local currency: PED - Project Entropia Dollars
- Exchange rate 10 PED – 1 USD
- Turnover of 3.6 Billion PED in 2006
- Real World Banks opened Virtual banks in Entropia Universe
- Trading and Business initiatives
Description
- Metaverse
- One person can use more than one Avatar.
- IM (Instant Messaging) enables an Avatar to send a message to a group of Avatars
Business& Culture - Virtual lands acquisition
- Virtual arts and museums Louvre
- Concerts performed by real artists
Susan Vega's concert was the first. - Software & Hardware vendors presenting their real world products
- Embassies of Real Countries
Moldav Islands, Sweden
- Local Crime
A Second Life Police role is to reduce the crime rate. - Improper Content e.g. Pronography
- Copyrights issues
- Biases in favor of large companies. Residents get less and pay more.
Example 3: Stagacoach Island CommunityThis Virtual World is the cornstone of a revolutionary marketing approach of Wels Fargo bank. The bank created a Virtual World called StagenCoach Island. Playing includes financial training. Marketing by creating a Virtual World is directed towards the younger generation or the Web generation.The Web Channel is more effective than traditional channels such as Newspapers or TV, because the younger people allocate much of their time for Web activities.
Future Directions
One direction is standardization. A new IBM & Linden Labs initiative of 3D Internet standards was joined by Cisco, Google, Sony, Intel, Multiverse, Microsoft, Motorola, Philips and academic reaserchers.
Stnadardization is one enabling element of The Virtual Grid.
The idea is crossing boundaries of Virtual Words by avatars, similar to citizens of a real country crossing a boarder to another country. These avatars should own virtual passport which will be checked by virtual workers at the gate of a Virtual World.The benefits could be more cooperative and innovative Virtual Universe, which eliminate the necessity to create multi Avatars for one real human.

No comments:
Post a Comment